Tim Murawski
CCO and President at Augmedics
During the HIV/AIDS era of the early 1990s, when healthcare workers were at risk from accidental needle sticks, Tim Murawski found his passion directed toward the life and safety-enhancing technology of the medical field. He has been employed with Baxter Healthcare's IV Systems Division, has been affiliated with Hansen Medical, and has been instrumental in helping to build other young medical technology companies from the ground up.
Tim Murawski's enthusiasm for, understanding of, and experience with disruptive technology proved to be the catalyst for a distinguished career in the field of medical robotics. Between 2010 and 2019, he held several positions, including Vice President of US Accounts and Vice President of Global Renaissance Business, with Mazor Robotics prior to its subsequent transition to Medtronic following a $1.6 billion acquisition, and he is known for his strategic management style and for building high-value product propositions.
Tim Murawski excels at "big picture" efforts and has been involved not only in leading-edge technology that results in surgical benefits but also takes time to mentor others and tries to inspire new leaders in the field.
Raised in the Chicago area as the fourth of five children, Tim Murawski says he learned the benefits of a strong work ethic at an early age from his working parents, and he believes his ability to "do what needs to be done," and to "see the big picture" have been instrumental to his success.
Tim Murawski shows no signs of slowing down. He lives with his wife of 35 years, and a dog, and he enjoys water skiing, tennis, and working in his yard in his free time.
 medium.com/@tim-murawski?source=rss-d810cde340be------2
medium.com/@tim-murawski?source=rss-d810cde340be------2
University of Birmingham Develops Long COVID Assessment Tool

COVID is like a monster that won’t go away. Although vaccines have limited the transmission as well as the occurrence of serious symptoms, there are still people that suffer with long COVID as well as those who die from the virus.
The University of Birmingham has recently developed a tool to assess the symptoms of long COVID in the hopes that they can produce a treatment that provides relief. Read on to find out more about this innovative technology.
What is Long COVID?
Long COVID is a characterized by lasting conditions that continue to occur after a person who once had the virus is no longer testing positive. Symptoms can last for months and may even be uncurable. More than 200 symptoms exist including breathlessness,fatigue, and brain fog.
The condition affects more than 100 million people worldwide accounting for around 30% of COVID survivors. Symptoms may be mild or severe. In some cases, they can even cause a disability.
The Survey
Researchers at the University of Birmingham developed a patient reported measure outcome or PROM to assess the symptoms of long COVID. It is meant to be completed by long COVID sufferers. It can be filled out by the individual, or it can be answered in interview form.
The survey was created based on identified long COVID symptoms which were validated by 10 clinicians. The symptoms were determined through publishedliterature, health practitioners and the patients themselves. The questionnaires were then field tested on 274 adults with long COVID.
How the Survey Will Be Used
The survey will be used to answer the question of whether long COVID is a single condition, or whether it includes multiple illnesses that fall under the COVID umbrella. It will make it easier to diagnose and treat patients.
It will primarily be used to contribute to a study being conducted on non-hospitalized individuals with long COVID utilizing data from the survey as well as measurements gathered from wearable devices and blood and biological testing.
Challenges Faced
Although the survey may be effective in treating long COVID, it is unknown whether it will provide enough data to address all aspects of the condition. It will be assessed alongside other data, however, there are many unknowns concerning how long symptoms last and how new variants will affect the development of long COVID. But, experts feel that the research results will begin to take center stage as scientists are better able to understand long COVID as a condition.
Another COVID Breakthrough
While the University of Birmingham works on developing their survey so it can be used routinely in clinical practice, Pfizer has come out with a COVID pill that will reduce hospitalizations by 89%. The US government has already placed orders for $10 billion of the new drug, Paxlovid.
The drug was designed by chemists to interfere with the virus’s ability to copy itself. It attaches to and blocks a protein called protease that assists the virus in replicating.
Protease enzymes exist in other types of coronaviruses so the drug may be effective in reducing the effects of the next pandemic that may arise due to pathogens similar to SARS that may be present in a variety of animal life.
While the drug wasn’t produced as quickly as the vaccine, it still sets records as a new molecule developed to defeat disease. It acceleratedfrom lab development to research to FDA approval. Pfizer CEO Albert Bourla reports that he was “in tears” after receiving news that the drug was effective.
Pfizer isn’t the only pharmaceutical company to carry a drug that can be used to prevent COVID from replicating. Merck carries one that targets a different mechanism in the virus’s mechanism system.
The drug will be effective in minimizing deaths and hospitalizations in people with weakened immune systems who are unable to take the vaccine. And if a new variant turns up that is resistant to the vaccine, it may be the only viable solution for keeping it under control.
Paxlovid is readily available by prescription only.
Conclusion
COVID continues to be a threat to wellness. Fortunately, developments are underway in the form of a survey that will assist with the diagnosis and treatment of long COVID as well as a pill that will prevent the virus from replicating. It is hopeful that this new technology will keep the disease under control once and for all.

When someone is suffering with a stroke or aneurism, it’s vital to get them the help they need when they need it. A time lapse can be a matter of life and death. But what happens when a surgeon is not around when they are needed?
Now, a new technology is being introduced that will allow surgeons to perform procedures virtually. It comes in the form of a joystick operated robot. Read on to find out more about this innovative, potentially life-saving solution.
How It Works
The telerobotic system was developed by MIT engineers. It allows surgeons in one hospital to use a modified joystick to control a robotic arm in another location so it can safely operate on patients in a critical window of time.
The robot’s movements are controlled by magnets. The system is designed to remotely perform endovascular interventions which are used to treat strokes caused by blood clots. The procedure involves manually guiding a thin wire to the clot to clear the blockage.
Stroke patients experience a golden hour which takes place directly after the stroke occurs. It is imperative to administer treatment within this period to minimize brain damage.
Many doctors are unable to reach patients at that time leaving them with permanent cognitive dysfunction. The robotic arm allows them to administer treatment virtually when it’s needed so damage is minimal or nonexistent.
Teams are hoping that the system could be installed in smaller hospitals and guided by doctors in larger medical institutions. The provider would use the joystick and live imaging to adjust the orientation of the magnet which is located on the wrist of the robotic arm. In doing so, they would guide the magnetic wire through vessels and arteries to clear the clot.
Studies conducted on the system show its potential. A transparent model that replicated the complex arteries of the brain was used for testing purposes. Neurosurgeons were able to virtually control the arm to enable the wire to reach the clot with just an hour of training.
Overcoming Challenges
While endovascular surgery is minimally invasive, it comes with its share of challenges. Guiding the wire to the targeted location is a precise procedure that can easily cause damage to surrounding vessels and arteries. It requires years of training.
Developers faced challenges in building a system that would be sophisticated enough to successfully perform the procedure. They referred to research conducted in 2019 which involved guiding a magnetically controlled thread through a life-sized model of the brain. A handheld magnet, about the size of a soup can, was manually manipulated in the experiment.
They built on earlier research by placing the magnet onto the robotic arm which can be manipulated with the joystick knob attached to a mouse. Users can tilt the joystick to change the magnet’s orientation, which in turn, directs the wire. The buttons on the mouse are used to make the wire move back and forth.
A conventional neurovascular wire is used as its soft, magnetically responsive tip will follow the magnet’s direction.
Testing Progress
Testing for the robotic arm is still underway, but so far, things look promising. An operating room in MGH’s Catheter Lab was set up with the robotic arm and the medical imaging equipment used in endovascular procedures. A monitor displayed a live video of the model allowing the operator to determine the path for directing the wire through the vessels.
The group of neurosurgeons involved were able to successfully guide the wire through the complex system of vessel.
They were also able to guide the arm to clear simulated clots in hard-to-reach areas going through vessels and around sharp corners. Once they arrived at their destination, they were successful in threading a microcatheter along the wire to the clot. The wire was retracted removing the clot and leaving the catheter behind to deliver therapeutics.
In addition to providing remote care to patients when they so desperately need it, the robotic arm will take surgeons out of operating rooms minimizing their exposure to harmful X-ray radiation.
Conclusion
The robotic arm being tested will save and improve lives of stroke victims. It provides an ideal way to overcome the limitation surgeons face when they can’t reach their patients at pivotal moments. It is a technology that will make for significant advances in the world of cardiovascular health.
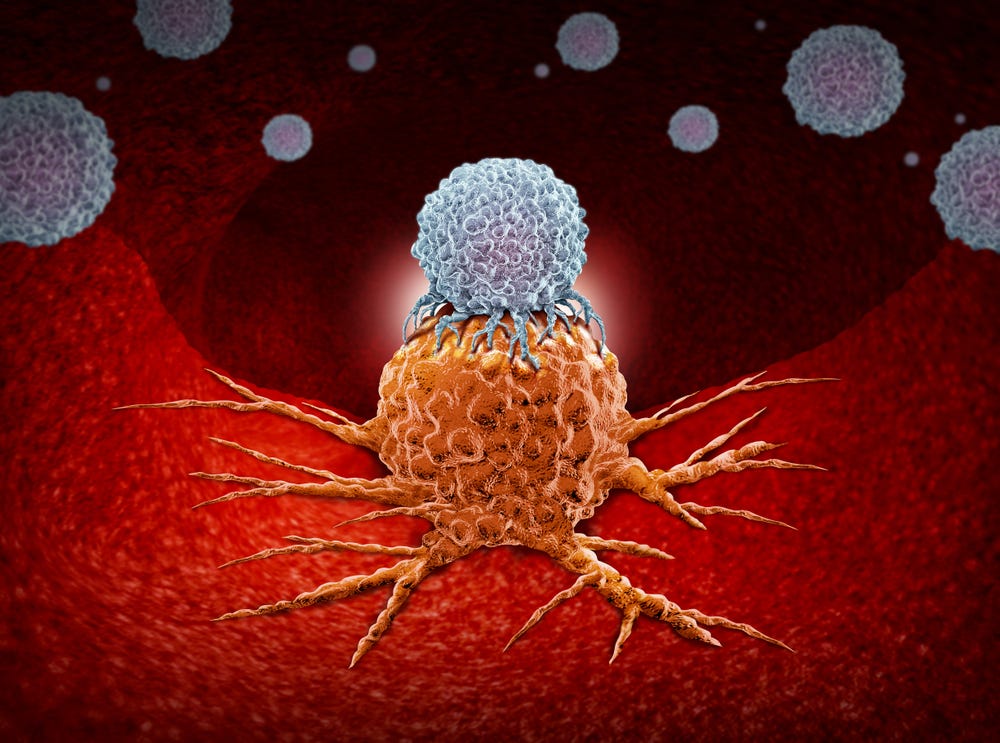
It used to be that tumors could only be treated through radiation, chemotherapy, surgery, and other medical techniques that came with their share of unpleasant side effects. Now histotripsy is emerging as a noninvasive sound technology method that has been shown to break down liver tumors, kill cancer cells and boost the immune system to prevent the spread of cancer. Read on to find out about the latest clinical trials involving this innovative technique.
The Research
Animal studies conducted at the University of Michigan show that histotripsy has the potential to destroy 50 to 75% of tumor volume enabling a rat’s immune system to eliminate the remainder. Over 80% of animals tested showed no evidence of reoccurrence or metastases.
Histotripsy involves using ultrasound waves to destroy cancerous tissue with millimeter precision. This relatively new technique is being tested in human liver cancer trials taking place in the U.S. and Europe.
The studies involve creating soundwaves similar to those used by an ultrasound device. A transducer, designed and built by U of M technicians, produces high amplitude ultrasound pulses that last just a microsecond, to break up tumors. They compare to ultrasound devices that use lower amplitude pulses for imaging.
The pulses create microbubbles in the tissues that expand and collapse rapidly to kill cancer cells and break up the structure of tumors without harmful side effects. After the treatment is complete, a robotic arm comes in for a point-by-point ablation in the targeted tumor area.
Many clinical trial situations make it difficult to target an entire cancerous tumor due to its size, location, or stage. The recent trials that involved histotripsy targeted only a portion of each tumor showing how the technique could be effective in less-than-ideal circumstances.
Liver cancer ranks in the top 10 in contributing to cancer related deaths worldwide. Five-year survival rates for the disease are less then 18% in the United States. There is a high likelihood of tumor recurrence and metastasis after initial treatment occurs.
It is hopeful that the recent study will lead to more research establishinghistotripsy as an effective treatment for liver cancer.
Histotripsy has been studied at the U of M Xu laboratory since 2001 for its potential to fight cancer. The latest clinical trial, #HOPE4LIVER is showing promising advances in the field. The technique may also be effective in brain therapy and immunotherapy.
How Long Has Histotripsy Been Around?
Histotripsy has been studied in research laboratories for about 15 years, but clinical trials have only just begun. Its roots can be traced back to lithotripsy which involves applying shock waves to break up kidney stones and part of the ureter. It can also be compared to thermal ablation which uses focused ultrasound.
When Can Histotripsy Be Used?
Theoretically, histotripsy can be used on any kind of tissue throughout the body that can be radiated with a focused ultrasound technique. However, it will be difficult to apply behind a bone as the ultrasound will reflect off the structure. It may also not be ideal for air-filled organs.
As more research is performed, it is hopeful that the technique will be updated with more accurate safety standards making it effective in the treatment of bladder tumors, kidney cancers and lymph node conditions.
Is Imaging Involved with Histotripsy?
Imaging may be used to determine the area to be targeted. It will allow providers to detect the tumor location so they can direct soundwaves in the desired location. It will make for effective online monitoring during the procedure.
What are the Benefits of Histotripsy?
Histotripsy does not produce unwanted side effects. It is noninvasive and, therefore, does not carry a risk of infection or require any incisions that need to heal. It is an outpatient procedure that requires follow up care that can easily be carried out if the patient lives close to the facility.
What are the Risks of Histotripsy?
Histotripsy does not have any associated risks if the procedure is carried out correctly. With poor planning, it is possible that the energy will be applied to the wrong area. But with the right visual tracking, this should not be an issue.
There is also the possibility that a patient could make an involuntary movement such as breathing or coughing while the procedure is taking place. Anesthesia is used to keep this from happening as it would cause an immediate intervention and the procedure would need to be rescheduled. In the future, technicians are hoping to replace full anesthesia with a simple sedation.
Conclusion
Liver cancer is responsible for far too many deaths each year. Histotripsy is showing to be a promising method for eliminating tumors and in producing other medical benefits. With further clinical trials improving is safety and efficacy, it may contribute to increased wellness and longevity among humans and animals.

In this episode, Dr. V welcomes Brooke Burke, television personality and fitness guru. The two discuss the female evolution that comes later in life.
What is Female Evolution in Your 40’s?
Aging comes with its share of downsides, but Burke explains to Dr. V how she embraces it as it gives women the perspective to figure out who they are. It allows them to establish boundaries and learn how to say no. It lets them take on an ‘I don’t give a f**k’ philosophy so they can put themselves first when need be.
Burke and Dr. V reflect on the issues that have held women back in the past. They look at their own mothers and determine that they may have been reluctant to speak up because they were sold on an idea of perfectionism. They were taught to fear failure.
Today’s women know that it is okay to fail because it provides a teaching experience. Failure is more accepted among women in modern times. And as you get older, you become more used to failing and may even embrace it and see it as a learnable moment.
On Marriage
Dr. V then asks Burke what she feels was the worst advice she ever received. Burke refers to her father who engrained her with the idea that marriage was for life. She feels that this is what made her stay with her husbands (Burke was married twice) when she really should have moved on.
She says that she saw leaving her marriage as a sign of failure. She describes being in a situation where she didn’t know what she wanted, how to express herself or define what she needed. She notes that there may have been confusion between intensity with passion and privacy and love.
Burke since realized that she needed to achieve peace in life and find a relationship that was easy for her. She has moved on to apartnership that she considers ‘easy’. She knows herself better as a person and doesn’t need the intensity of an ‘up and down’ relationship and feels this makes for a healthier union.
Celebrating Life
The conversation then rolls around to the concept of celebrating life. Burke and Dr. V realize that being faced with their longevity may increase the need to be happy. This feeling of celebration is something they believe they can produce within themselves and within their relationships.
They then pose the question, are young womencelebrating enough? They wonder if they are holding back due to a lack of being comfortable in their bodies. This is something they refer to as a ‘pleasure gap’ between younger and older generations.
Burke and the doctor further dissect the pleasure gap by taking it to the bedroom. Dr. V notes that 94% of women do not orgasm during intercourse. Burke capitalizes on this commenting on how many women have accepted that they cannot orgasm and will never experience ecstatic pleasure and feel intercourse is about ‘his’ pleasure.
Burke says that this is not okay. She believes that women need to break away from the construct of women not experiencing pleasure. Thetwo emphasize the need for women to feel comfortable within their own bodies so they own their pleasure.
Talking More Openly
This takes Burke onto a related topic of how today’s older women feel comfortable talking about sexual pleasure. They believe this may be a difficult subject for younger women to broach as they are involved with small children and other tasks. Once they get older, they can focus on themselves and be open about what makes them feel good.
The increased openness allows them to “bring a much more rounded woman to the table”. They have the freedom to be who they are supposed to be, and this is something they wish younger women understood. This is advice they would have given to their younger selves and would share with their daughters.
What Should Women Be Looking for in Relationships?
The women move on to reflect on what women should be looking for in a relationship. Brooke comments that she enjoyed it when her current partner told her she could feel safe with him. This brought a different perspective to the relationship, and it was something she was missing in her past partnerships.
She also appreciated his generosity with his feelings and his sense of openness. This is something that she is thankful for. It’s also a sign that she’s willing to give and accept love.
Conclusion
Burke and Dr. V encourage women to better understand themselves and own their feelings. They recognize this as something achievable with age but encourage women to embrace it earlier in life. Listen to the podcast in its entirety to find out more about how evolution can help you achieve the happiness you deserve.

If you look at the causes of most diseases and illnesses, genetics often takes a front seat. People who have relatives with a certain condition are likely to have it handed down to them.
It used to be that there wasn’t anything you could do if you were predisposed for a certain condition. But gene therapy has changed all that. It involves correcting the underlying genetic disorder to treat a disease. It is an effective alternative to drugs and surgery.
This article will look at what’s involved in gene therapy and what we can expect for the future of this technology.
What is Gene Therapy?
Also called gene transfer or gene addition, gene therapy was originally performed using the following methods:
· Introducing a new gene to help fight a disease.
· Introducing a copy of a faulty gene to replace the one causing the disease.
With advances in technology, a newer type of gene therapy technique was introduced known as genome editing. It uses a slightly different approach. Instead of adding new genetic material to the body, it utilizes molecular tools to change a cell’s DNA. It has the potential to:
· Fix a genetic alteration that may be causing a disorder to ensure proper gene function.
· Activate a gene to assist in fighting a disease.
· Turn off a gene that’s not functioning properly.
· Remove a piece of DNA that’s interfering with gene function and causing disease.
Gene therapy has shown to be effective in treating some diseases including the eye disorder Leber congenital amaurosis and the muscle disorder spinal muscular atrophy. Research is being conducted to determine its safety and efficacy in treating other illnesses and conditions.
What are the Various Types of Gene Therapy Products?
There are various types of gene therapy products that can be used to improve health. They include:
· Plasmid DNA: This involves circular DNA molecules that are genetically engineered to introduce therapeutic genes to the cells in the body.
· Bacterial Vectors: In this process, bacteria are modified to prevent infectious disease. They are then introduced to the body and used as vehicles to carry healthy genes to tissue.
· Viral Vectors: This technique uses viruses that have been modified to eliminate their potential to carry infectious disease as vehicles to carry therapeutic genes to tissue.
· Patient Derived Cellular Gene Therapy Products: These are cells that are removed from the patient, genetically modified, and then placed back into the patient’s body.
· Human Gene Editing Technology: This works to disrupt harmful genes and repair mutated ones.
In Vivo Gene Therapy vs. Ex Vivo Gene Therapy
Currently, a lot of attention it being paid to in vivo gene therapy. It different from ex vivo gene therapy which involves cells being removed from the body and sent to a lab where they are altered. With in vivo therapy, the new material is created and inserted into the body directly via an injection into the blood or a targeted organ.
Ex vivo therapy is mostly used to treat blood related disorders such as leukemia and lymphoma. It is currently being researched for its potential to treat sickle cell anemia in children. It aims to lower the activity of BCL11A, which contributes to abnormal red blood cell production.
In vivo therapy is used for genetic disorders that affect one specific organ of the body making it effective in treating heart and eye conditions as well as spinal muscular atrophy. It involves injecting healthy genes directly into the affected area. It is currently being studied for its potential to treat hemophilia A.
Ex vivo and in vivo therapy both have their share of advantages and disadvantages. Ex vivo therapy allows providers to control the process of creating new genetic material. You can verify that new genetic material is healthy before it is introduced to the patient.
However, preparing cells outside the body can be difficult and time consuming. It also can be difficult to target the necessary internal organs.
In vivo techniques are less complicated since the cells don’t need to be removed from the patient. The process also makes it easier to target internal organs.
However, it requires a very precise delivery of genetic material to the targeted area. If delivery is not precise, it can result in an immune response.
Conclusion
Gene therapy is making waves as an effective and permanent way to treat disease. So far, it’s scope is limited, but it’s hopeful that advances in research will make it a more popularly used technique. It has the potential to increase longevity and quality of life worldwide.

The world of healthcare is becoming more digitized. Electronic medical records are being used, virtual appointments are being scheduled and internet connected devices are being used in examination rooms. Well, what if I told you that these are all part of a connected ecosystem known as the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)?
Read on to find more about this network and how it works.
What is the Internet of Medical Things?
IoMT is a network that includes wearables and devices that are connected to the internet as well as electronically stored patient information. Its rise is attributed to an increase in medical devices that can collect, generate,analyze, and transmit health data and images and connect to provider networks via the cloud or an internal service. It results in more efficient clinical management and an improvement in patient care.
The IoMT can be categorized into a variety of segments including the following.
On-Body: On-Body refers to wearables. These include consumer health wearables like Fitbits and other types of bands, watches and garments that measure vitals as you exercise. It also encompasses clinical grade wearables that are generally provider recommended and FDA approved. They are made to detect falls, stimulate brain areas during workouts and provide pain relief.
In-Home: In-home refers to remote patient monitoring which is used for chronic disease management, telehealth visits that replace in-person exams and emergency response systems which mobilizeemergency services if a dangerous situation is detected.
Community: The community segment is made up of five components including the following:
· Mobility which tracks patients’ health via passenger vehicles during transit.
· Emergency Response Intelligence which assists first responders, hospital emergency staff and paramedics.
· Kiosks which can dispense products and provide remote services via a touchscreen.
· Point of Care Devices which are defined as devices used by a provider outside of a traditional healthcare setting.
· Logistics which refers to the transport and delivery of health care products and services.
In-Clinic: In-clinic IoMT are the devices designed for administrative or clinical functions. They are used directly in the office and allow providers to access and record data via a cloud-based system. They also provide capabilities so members of staff can be located remotely.
In-Hospital: Here are the IoMT functionalities that may be used in a hospital setting:
· Asset Management which monitors and tracks valuable equipment throughout the facility.
· Personnel Management which measures a staff’s productivity and efficiency.
· Patient Flow Management which ensures patients are moving seamlessly through the healthcare process.
· Inventory Management which keeps track of supplies and medications.
· Environment which ensures the atmosphere in the hospital is healthy and running with maximum energy efficiency.
Benefits of the IoMT
The IoMT has produced countless benefits in the healthcare space. Here are some to consider.
Lowers Costs: The IoMT has resulted in more online office visits which save patients and providers time and money. Goldman Sachs estimates that the healthcare industry can save $300 billion annually due to remote patient monitoring and improved medication guidance.
More Accurate Diagnosis: A study conducted by researchers from UCLA and Cedars Sinai Medical Center shows that Fitbit trackers’ ability to record heart rate and accelerometer data simultaneously yields an improvement in evaluating patients with ischemic heart disease. This has led to 88% of health providers investing in remote patient monitoring devices.
Improved Drug Management: The IoMT includes the use of smart pills that contain microscopic sensors. Once swallowed, they can transmit health data to connected devices. This allows providers to keep track of patient health and oversee medication adherence.
The Future of IoMT
With all the benefits IoMT can provide, it should come as no surprise that it is poised for significant growth in the coming years. The market was evaluated at $44.5 billion in 2018 and that number is expected to rise to 254.2 billion by 2026.
Trends that will be taking over include wearable devices such as smartwatches and smart shirts. There will also be a rise of AI integrated into connected devices that can provide measurements and analysis of data in real time.
It will also pave the way for new technologies like kiosks that connect patients with care providers and facilitate remote care. These will be a huge benefit for rural communities that are short on medical clinics and resources.
Conclusion
With all that IoMT can provide, it’s no surprise that it’s growing in leaps and bounds. Its ability to boost efficiency and lower costs is revolutionizing the world of healthcare. We can only wait to see where it will take us in the future.

In today’s world of healthcare, doctors are putting an emphasis on the importance of patients becoming accountable for their health. This requires physicians educating their patients. Once individuals become knowledgeable about their conditions and bodies, they can get proactive with selfcare and step up when it comes to improving their quality of life.
Thyng LLC, an augmented reality app company has recently launched a body tracking technology that educates individuals about their anatomy taking a fun and interactive approach. MedMirror is a freestanding display that uses advanced body tracking to enhance the digital healthcare journey. Read on to find out more about this innovative tool.
How Does MedMirror Work?
Patients who wish to use MedMirror can simply stand in front of the mirror. A 3D view of their anatomy will automatically be overlaid on to their bodies so they can ‘see’ into their systems. This allows them to better understand the relationships between parts of their anatomy as well as their medical conditions.
The mirror also has an alternate feature that allows pediatric patients to become their favorite superheroes or interact with their favorite characters and mascots. This is meant to reduce the stress associated with long hospital stays. It is perfect for lobbies, waiting rooms and children’s hospitals.
Benefits of MedMirror
MedMirror offers a variety of benefits including the following:
· Helps users learn about their body parts
· Helps users understand how the various systems of the body work including the circulatory system, the respiratory system, and the digestive system
· Educates users on general conditions like heart conditions, tumors, broken bones, andtheir possible treatments
· Allows users to become and/or interact with superheroes and characters to reduce stress and anxiety.
“MedMirror creates a new level of understanding and inspiration with patients. Allowing for better education and creating an environment where the spirit is uplifted,” says Ed LaHood, CEO of Thyng.
“Patient education is crucial. Engaging with innovative tools like MedMirror improves our interactions. Not only does it educate but can reduce anxiety in the pediatric age group who are in an unfamiliar place,” said Dr. Jonathan Morris, neuroradiologist and medical director of Advanced Biomedical Visualization and Experiential Learning and Mayo Clinic.
The Importance of Patient Engagement
MedMirror is vital in increasing patient engagement. Patient engagement is important for the following reasons.
· Reduces Burden on Staff: When patients are engaged, they take their healthcare responsibilities into their own hand. This puts less burden on staff so they can deal with more pressing issues.
· Leads to Better Health Outcomes: When patients are engaged, they are more likely to attend health appointments and participate in regular health screenings. They are also more likely to research information about their health outside of appointments.
· It Cuts Down on Cost and Waste: Most patient engagement tools are provided virtually which cuts down on waste and cost.
· It Makes Patients More Satisfied: Patients that are engaged in their own healthcare tend to be happier with the treatment they receive. This makes them more likely to become loyal to their providers and to refer them to friends and family.
Other Ways to Increase Patient Accountability Through Technology
MedMirror educates patients so they are better able to take responsibility for their health. But this is not the only way technology has produced a shift.
The COVID pandemic has caused an increase in virtual healthcare. Now that much of the world is in its endemic stages, individuals continue to turn to telehealth for the convenience it provides.
Doctors who use virtual platforms have noticed an increased accountability on patient’s behalf’s. They must take responsibility in terms of preparing for the visit, examining themselves and generating their own health data. While some patients fall behind with the added weight on their shoulders, many have stepped up to the plate.
Providers have also been taking steps to making patients more engaged in the healthcare process. They feel this is a key driver to the outcome of healthcare treatments. As a result, they have creating virtual waiting rooms to increase patient readiness at the time of the appointment, and they attempt to maintain patient attention through storytelling and emotional connectivity.
Conclusion
Patient engagement and education is critical in producing positive healthcare outcomes. Tools like MedMirror and other virtual developments provide the technology individuals need to become accountable for their well-being. It will be interesting to see how future developments lead to innovations in this space.

Technology is becoming more integrated in the world of healthcare. Providers often use digital formats to store patient information and to offer treatment. This has led to increased convenience, but it also poses a greater cybersecurity risk. Healthcare agencies must step it up to ensure they protect patient information.
This article will review the risks and the efforts being taken while looking at the future of cybersecurity measures in the industry.
The Importance of Cybersecurity and Patient Safety
Any business that takes its operations online is prone to cyberattacks, but the healthcare industry is especially vulnerable. This is because providers possess so much sensitive patient information. This includes protected health information, financial information and personally identifying information like social security numbers.
Because health records are so informative, they may sell for up to 10 times more than stolen credit card numbers on the dark web. And the cost for health care companies to remediate a breach can be three times higher than costs incurred in other industries. On average, it costs about $148 to recover a stolen non-health record as compared to $408 for a health record.
Cyberattacks also get in the way of a provider being able to care for their patients. For example, the May 2017 “WannaCry” ransomware attack resulted in several ambulances being diverted and surgeries being canceled.
What Can Providers Do to Increase Cybersecurity?
With cybersecurity being so crucial to healthcare providers, steps must be taken to up the game. These include the following:
· Cybersecurity Training for Staff: Offices must train their staff so they can recognize signs of phishing and spoofing.
· Apply Software Updates: Software updates are often made to make systems more secure. Any delay in applying these updates can leave your system vulnerable to attack. The best practice may be to set your system for automatic updates.
· Delegate Employee Duties: The more people that have access to your information, the more likely it will be to leak. This includes your employees. So if one employee is in charge of financials, there’s no reason to provide them with information on patient history and other extraneous data. This will only increase your vulnerability.
· Password Management: It’s a basic rule, but it’s worth repeating. Providers should come up with unique passwords for each system and account. Passwords should be changed every 3 months.
· Perform Regular Risk Assessments: Risk assessments should be performed at least once a year so you can determine new threats and decide if updated technology is necessary.
· Utilize Various Forms of Security: Medical businesses are advised to use multiple forms of protection so if an attacker circumvents one security measure, there will be others in place to prevent an attack.
· Enforce Data Recovery: Cyberattacks often lead to a loss of data which can be crippling for a medical provider. A backup system must be used to ensure data is kept intact in the event of an incident.
· Keep Mobile Gadgets Protected: We often think of protecting computers and laptops, but mobile devices like tablets and gadgets should not be overlooked. In fact, protection on these should be ramped up as they can be easily stolen. It’s best to keep any sensitive data off a mobile device, but if the need arises, the data should be encrypted.
The Release of the FDA’s Draft Cybersecurity Guidance
The government is also doing its part to increase cybersecurity in the healthcare space. This comes in the form of the FDA draft guidance which replaces a 2018 document. It provides a cybersecurity approach with recommendations for how medical device manufacturers should deal with security in premarket submissions to maintain security in software-based products once released.
While the draft is not legally enforced, medical device manufacturers will need to adhere to the FDA’s cybersecurity expectations to gain premarket approval. It emphasizes the lifecycle of the product from submission to deployment in terms of digital safety issues. It also addresses older products that were not created with security in mind.
The draft guidance is still being reviewed, but once released, it will cause manufacturers to take a closer look at their products and determine their shortcomings in terms of security issues. It also recommends that threat modeling be carried out during the design process. This has previously been a weak spot in the industry, and it is believed that these new guidelines will produce an improvement in that area.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity is vital in the healthcare industry. Fortunately, there are several steps that can be taken to keep patient information safe. It is hopeful that this increases to improve systems as time goes on.

Pacemakers have long been used in the healthcare industry. These small devices are implanted in the chest to replace or regulate the heart’s functions. They can be lifesavers in many situations.
There have been several advances in pacemakers as technology moves forward. One example is the smart pacemaker that works to better adapt to the body’s demands. Read on to find out how these upgraded devices are revolutionizing the MedTech space.
Smartphone Enabled Pacemakers
One development involves allowing patients to use a smart device app to monitor pacemakers remotely. This has yielded a higher rate of scheduled transmission success as compared to traditional manual and automatic bedside monitoring technology.
The technology works by providing patients with the ability to use an app-based platform to transfer the data collected by their pacemakers to patient management networks without traditional bedside monitoring. End to end encryption is used to keep the data secure. It also offers patients information about their pacemaker including its activity tracker data and transmission history.
Studies have been conducted to determine smartphone enabled pacemaker success rates among patients. Results showed that the pacemakers yielded a 92.8% to 94.6% success rate in scheduled transmissions. Although more testing is needed to determine pacemaker adaption in the industry, findings have been positive thus far.
Experts feel that the electronic devices will empower patients with the knowledge of their health status while providing a more convenient and reliable system of monitoring. They also feel that the devices will be less daunting for patients to use.
Smart Pacemakers to Prevent Heart Failure
Pacemakers are generally used to treat arrythmias (irregular heartbeat). They can rarely treat more severe conditions like heart failure that occurs when the heart is not pumping as strongly as it should.
Most pacemaker rely on activity sensors that detect the patient’s motion. But they are not advanced enough to pick up on the variations in heart rate or the brain activity that controls heartrate. Therefore, a pacemaker could detect that a person is at rest when they are actually exercising.
These are the types of limitations that do not allow pacemakers to address more advanced conditions.
But all that may be about to change due to, CResPace, an H2020 project funded by European Union. Researchers have developed a smart pacemaker that is supported by artificial nerve cells to re-synchronize the heart. The bionic neurons allow the pacemaker to adapt to the body’s demands including exercise activities and psychological signals from the brain.
The artificial nerve cells that are used in the newly developed pacemaker has also shown promise in the treatment of neurological degeneration and in helping people overcome paralysis by restoring failed brain circuits. It may also be integrated into studies of a technology that allows people to control computers via mindpower.
So far, the smart pacemaker CResPace has developed has successfully been tested on animals. Teams are now looking to move forward to human studies.
Transient Pacemaker That Harmlessly Dissolves in the Body
Yet another advancement comes in the form of a transient pacemaker that dissolves in the body when it is no longer needed. It is wireless and battery free.
The lightweight, flexible device is recommended for patients that need temporary pacing after cardiac therapy or while waiting for a permanent pacemaker. It naturally absorbs into the body within five to seven weeks without requiring surgical extraction.
The device works by harvesting energy from an external remote antenna that uses nearfield communication protocols. This is the same technology used in RFID tags and by smartphones for electronic payments. It eliminates the need for large batteries and rigid hardware that can include leads that cause infections.
The transient electronics used in the device can open a new chapter of medicine. It can lead to the development of a variety of transient devices that can be used for diagnosing and monitoring diseases and administering medications and therapies.
The newly developed device is just 250 microns thick and weighs less than half a gram. It is soft and flexible, and it laminates the heart surface to deliver an electrical pulse. It is implanted on the surface of the heart and can be activated remotely.
If successful, the transient pacemaker will provide recovering patients with increased comfort and mobility and offer an improved rehabilitation period.
Conclusion
The pacemaker is a lifesaving device. It’s wonderful to see that steps have been taking to make it more versatile, more convenient, and more patient friendly. We look forward to seeing how the technology grows with future developments.

When you hear the world blockchain, you thinkof cryptocurrency and video games. But, more recently, the technology has been adopted into the medical field yielding countless benefits for doctors and patients.
Blockchain is most synonymous with the cryptocurrency boom. It is a decentralized and secure way of transferring and storing data. While it has not yet been fully integrated into other industries, it is suspected that it will soon be embraced by the medical industry making the market worth a total of $200 billion by 2030.
Read on to find out how blockchain is being integrated into healthcare and the benefits it may provide.
How is Blockchain Being Used in the Medical Industry?
Blockchain is most commonly used to keep medical data safe and secure. This is essential in the healthcare industry considering that over 176 million patient records were exposed to data breaches between 2009 and 2017. Hackers will go after testing and health records as well as banking and credit card information.
The technology is effective in that it provides a secure and decentralized means of storing patient data. The identity of the individual is concealed through complex codes that offer advanced security. The decentralized format also allows for the easy sharing of information between doctors, patients and other healthcare providers that may have access.
Although blockchain is currently being integrated predominantly in the management of medical records, there is no saying how far it can be taken in the future.
Benefits of Blockchain
Blockchain provides many benefits to the medical industry. Here are some to consider.
Prevents Costly Mistakes
Miscommunication between medical professionals can cost the industry up to $11 billion dollar annually. It results in time consuming damage control and it can delay patient care.
The decentralized nature of blockchain makes for one ecosystem where data can be efficiently referenced by providers. This leads to more streamlined communication, that makes for faster diagnoses and more advanced customized care.
Improved Medical Supply Chain Management and Drug Traceability
Drugs are commonly used to treat illness, but how safe are the drugs we are using? Can providers be sure that they haven’t been tampered with? Are they certain that they are sourced from a legitimate supplier?
Blockchain can assist with supply chain management and ensure transparency in the shipping process. Once the drug’s ledger is created, the technology can be used to trace it as it moves through handling and delivery. It can also monitor labor costs and waste emissions to make dispersal processes more efficient.
Breakthroughs in Human Genomics
Genomics are set to play a vital role in the improvement of human health. A genome is a complete set of nucleic acid sequences encoded as DNA that can be found in the chromosome pairs in cell nuclei and in the small DNA molecule found in the mitochondria. Studying these genomes could open up doors in the medical research field.
In the past, processing a singlegenome cost about $1 billion. Today, costs have gone down to about $1000 and DNA testing companies are taking advantage of lower prices by providing individuals with test results that uncover clues about their health and ancestry.
Blockchain is an ideal fit for the genomics industry as it can safely store billions of genetic data points. It can even offer a marketplace where people can sell their genetic information to create a large data base that scientists can access for research. This will make the study of genomics more efficient, and it will open doors for improving human health.
It Can Help in the Case of Pandemics
The pandemic has lasted a lot longer than most anticipated, and it’s not over yet. And when it comes to the spread of viruses, who knows what the future may hold?
Studies have shown that blockchain may reduce the spread of disease in several ways.
Many countries have a system where they report an incident of infectious disease to government authorities. Before reports are made, they are passed through hospitals and clinics making for a system that’s prone to hacking and alterations that can lead to misinformation.
Blockchain technology would ensure the information goes directly to the source while reducing the risk of hacking and eliminating the possibility of editing data.
It also provides a digital way to store information which minimizes the need to deliver data by hand, a still popular form of communication in some countries. This would reduce face to face contact that can spread disease.
The blockchain would also store information regarding donations. The advanced security would help protect donor financial information reducing the risk involved in providing monetary aid to people in need.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is the way of the future. While most think of its uses in terms of cryptocurrency and video games, its ability to protect sensitive data is creating forward moving benefits for the medical industry. It will be interesting to see how it continue to play an important role in the healthcare spectrum as time goes on.
